Do My Sub Contractors Need To Be RRP Certified?
 There has been a lot of confusion regarding the details of the EPA RRP rule. One that seems to pop up over and over is certification requirements for sub contractors. There are two different certification considerations regarding sub contractors; firm certification and worker certification. Let’s take a look at each separately.
There has been a lot of confusion regarding the details of the EPA RRP rule. One that seems to pop up over and over is certification requirements for sub contractors. There are two different certification considerations regarding sub contractors; firm certification and worker certification. Let’s take a look at each separately.
Firm Certification for Sub Contractors:
The EPA is very clear on this. The following question and answer comes from the EPA web site’s FAQ page:
Question: My firm performs renovations covered by the RRP rule, but solely in the capacity of a subcontractor. If the general contractor is a certified firm, does my firm also have to be certified, or can we just provide the certified renovator?
EPA Answer: All firms performing, offering, or claiming to perform renovations covered by the RRP rule must be certified. In this case, both the general contractor and subcontractor must become certified firms.
 Whether working for the general contractor as a trade partner or a 1099 sales person (offers the work), sub contractors must become certified firms by apply for certification through the EPA. Ensuring that the subs they use are certified firms is particularly important for general contractors, because as part of the required documentation under the rule, the renovation checklist must include the names of all workers who participated in RRP activities on the job. If a sub contractor and his workers do work on the job and the sub’s firm is not certified, the EPA will easily be able to find both the general contractor and the sub in violation of the rule. If a general contractor knows that subs must be certified firms, hiring a non-certified firm to work on a job becomes a knowing and willful violation of the rule, which brings with it serious penalties. It’s also one easy way for a customer’s lawyer to suggest the contractor is/was negligent.
Whether working for the general contractor as a trade partner or a 1099 sales person (offers the work), sub contractors must become certified firms by apply for certification through the EPA. Ensuring that the subs they use are certified firms is particularly important for general contractors, because as part of the required documentation under the rule, the renovation checklist must include the names of all workers who participated in RRP activities on the job. If a sub contractor and his workers do work on the job and the sub’s firm is not certified, the EPA will easily be able to find both the general contractor and the sub in violation of the rule. If a general contractor knows that subs must be certified firms, hiring a non-certified firm to work on a job becomes a knowing and willful violation of the rule, which brings with it serious penalties. It’s also one easy way for a customer’s lawyer to suggest the contractor is/was negligent.
Note: Both Massachusetts and Rhode Island have this same requirement for sub contractors.
Worker Certification for Sub Contractors:
Again, the EPA is very clear on this. The following question and answer comes from the EPA web site’s FAQ page:
Question: Under the RRP Rule, can a certified renovator supervise workers of a different company, or must each firm involved in a project furnish a certified renovator?
EPA Answer: All firms performing renovations must ensure that all individuals performing renovation activities on behalf of the firm are either certified renovators or have been trained by a certified renovator. The RRP Rule does not prohibit firms from reaching agreement on which will supply the certified renovator who is responsible for ensuring compliance with the RRP Rule and who directs and trains non-certified workers. All firms remain liable for ensuring compliance with the RRP Rule.
Who is Liable, The General Contractor or the Sub?
The following question and answer provides clarification regarding the responsibility and liability of the business that is acting as the general contractor:
Question: Is the certified renovator assigned to a specific project responsible for the work practices of other contractors on the project if the certified renovator is an employee of the general contractor of the project?
EPA Answer: All firms performing renovations must ensure that all individuals performing renovation activities on behalf of the firm are either certified renovators or have been trained by a certified renovator. A firm acting as a general contractor may satisfy this requirement by hiring another certified firm that takes responsibility for ensuring that all individuals performing the renovation activities are either certified renovators or have been trained by a certified renovator. With respect to assigning a certified renovator who is responsible for any on-the-job training and regularly directing workers who are not certified renovators, a firm acting as a general contractor my satisfy this requirement by hiring another certified firm that in turn assigns a certified renovator to the job. However, this does not discharge the general contractor's liability to ensure compliance with the Renovation, Repair, and Painting Rule.
Note: The answer above also applies in Massachusetts, but does not apply in Rhode Island. In Rhode Island, the RI Lead Hazard Control Standard (Section 14.0) requires the Licensed Lead Hazard Control Firm (LHCF) to have a RI licensed Lead-Safe Remodeler/Renovator (LRM) designee as a condition of licensure.
 EPA has recently updated recognition of the 3M™ LeadCheck™ for use on drywall and plaster. Below are the specific instructions from the manufacturer, 3M, for conducting testing of drywall and plaster for lead. These instructions must be followed by the certified renovator for the test results to be recognized under the RRP rule by EPA. I think the key point to remember when doing such testing is that you are testing the paint, not the drywall:
EPA has recently updated recognition of the 3M™ LeadCheck™ for use on drywall and plaster. Below are the specific instructions from the manufacturer, 3M, for conducting testing of drywall and plaster for lead. These instructions must be followed by the certified renovator for the test results to be recognized under the RRP rule by EPA. I think the key point to remember when doing such testing is that you are testing the paint, not the drywall: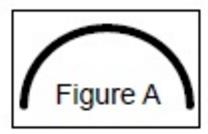 a) With a clean utility knife, make a nickel sized half circle cut at a low angle (about 5 degrees) cutting down to the bare drywall (gypsum) and plaster core to expose all layers of paint. Make the cut as seen in figure A.
a) With a clean utility knife, make a nickel sized half circle cut at a low angle (about 5 degrees) cutting down to the bare drywall (gypsum) and plaster core to expose all layers of paint. Make the cut as seen in figure A.
 Looking for accurate information about the EPA RRP rule?
Looking for accurate information about the EPA RRP rule? 
 There has been a lot of confusion regarding the details of the EPA RRP rule. One that seems to pop up over and over is certification requirements for sub contractors. There are two different certification considerations regarding sub contractors; firm certification and worker certification. Let’s take a look at each separately.
There has been a lot of confusion regarding the details of the EPA RRP rule. One that seems to pop up over and over is certification requirements for sub contractors. There are two different certification considerations regarding sub contractors; firm certification and worker certification. Let’s take a look at each separately. Whether working for the general contractor as a trade partner or a 1099 sales person (offers the work), sub contractors must become certified firms by apply for certification through the EPA. Ensuring that the subs they use are certified firms is particularly important for general contractors, because as part of the required documentation under the rule, the renovation checklist must include the names of all workers who participated in RRP activities on the job. If a sub contractor and his workers do work on the job and the sub’s firm is not certified, the EPA will easily be able to find both the general contractor and the sub in violation of the rule. If a general contractor knows that subs must be certified firms, hiring a non-certified firm to work on a job becomes a knowing and willful violation of the rule, which brings with it serious penalties. It’s also one easy way for a customer’s lawyer to suggest the contractor is/was negligent.
Whether working for the general contractor as a trade partner or a 1099 sales person (offers the work), sub contractors must become certified firms by apply for certification through the EPA. Ensuring that the subs they use are certified firms is particularly important for general contractors, because as part of the required documentation under the rule, the renovation checklist must include the names of all workers who participated in RRP activities on the job. If a sub contractor and his workers do work on the job and the sub’s firm is not certified, the EPA will easily be able to find both the general contractor and the sub in violation of the rule. If a general contractor knows that subs must be certified firms, hiring a non-certified firm to work on a job becomes a knowing and willful violation of the rule, which brings with it serious penalties. It’s also one easy way for a customer’s lawyer to suggest the contractor is/was negligent. While at the workshop I found one thing the main instructor Darcy Cook of Safety Trainers said to be very important for contractors to be aware of. Under the OSHA Lead in Construction Standard, contractors must assume their employees will be exposed to lead above OSHA’s established action level requiring the use of respirators until they actually conduct air monitoring testing to prove otherwise.
While at the workshop I found one thing the main instructor Darcy Cook of Safety Trainers said to be very important for contractors to be aware of. Under the OSHA Lead in Construction Standard, contractors must assume their employees will be exposed to lead above OSHA’s established action level requiring the use of respirators until they actually conduct air monitoring testing to prove otherwise.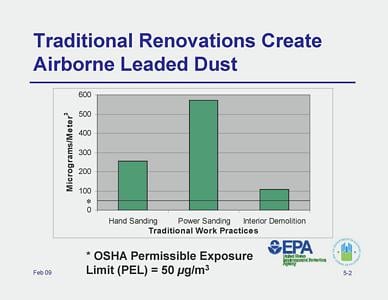
 So, under OSHA requirements, before allowing them to do RRP related work or even enter a contained work area, employees must first be sent to a physician to be sure they are healthy enough to wear a respirator. Then they must be fit tested by a professional and provided with a properly fitted respirator that protects them from worst case lead exposure scenarios based on the kind of work they do. They must also be trained how to select, use, clean and store a respirator. And, they must wear the respirator until the air monitoring testing is done to identify when a respirator is required and when it is not depending on how the work is performed and what engineering controls are being used.
So, under OSHA requirements, before allowing them to do RRP related work or even enter a contained work area, employees must first be sent to a physician to be sure they are healthy enough to wear a respirator. Then they must be fit tested by a professional and provided with a properly fitted respirator that protects them from worst case lead exposure scenarios based on the kind of work they do. They must also be trained how to select, use, clean and store a respirator. And, they must wear the respirator until the air monitoring testing is done to identify when a respirator is required and when it is not depending on how the work is performed and what engineering controls are being used. Renovators should be aware that in addition to EPA or administering states, other individuals or entities may likely take advantage of the documentation requirements to hold renovators accountable for their actions or lack thereof.
Renovators should be aware that in addition to EPA or administering states, other individuals or entities may likely take advantage of the documentation requirements to hold renovators accountable for their actions or lack thereof. OSHA could use RRP paperwork to prove non-compliance with its Lead in Construction Standards. OSHA’s worker protection requirements related to lead are very specific. Information contained in the required RRP documentation, particularly the renovation checklist and non-certified worker training documentation, could easily be used to show workers were not adequately trained and or protected when working in contained work areas. A lack of the required documentation could also be used by OSHA to demonstrate negligence by the business.
OSHA could use RRP paperwork to prove non-compliance with its Lead in Construction Standards. OSHA’s worker protection requirements related to lead are very specific. Information contained in the required RRP documentation, particularly the renovation checklist and non-certified worker training documentation, could easily be used to show workers were not adequately trained and or protected when working in contained work areas. A lack of the required documentation could also be used by OSHA to demonstrate negligence by the business.  I recently completed a series of seven videos about the new EPA RRP rule. The RRP videos were done for Remodeling magazine. They are posted to the Remodeling TV area of Remodeling magazine’s web site.
I recently completed a series of seven videos about the new EPA RRP rule. The RRP videos were done for Remodeling magazine. They are posted to the Remodeling TV area of Remodeling magazine’s web site. writing the script, interviewing contributors, editing the script with the magazine’s editor Sal Alfano, reviewing the raw footage, and working with the videographer,
writing the script, interviewing contributors, editing the script with the magazine’s editor Sal Alfano, reviewing the raw footage, and working with the videographer,  As like many of you, I have definitely exposed my body to lead over the last 30 plus years I have been involved in remodeling. As I learn more about lead poisoning and the symptoms of lead poisoning, I flash back to my younger years working for my dad’s remodeling business. Back then there was little awareness or thought given to the way we worked when disturbing lead paint. One summer I remember complaining of stomach aches, muscle pains and constantly feeling tired even after having the weekend off. My parents took me to the doctor but the doctor couldn’t find any reason for these symptoms. He gave me a terrible tasting medication to take daily and asked me to report back on how I was doing. The symptoms would seem to come and go all summer long, but then went away when I went back to college after the summer was over. This same scenario played over again the following summer.
As like many of you, I have definitely exposed my body to lead over the last 30 plus years I have been involved in remodeling. As I learn more about lead poisoning and the symptoms of lead poisoning, I flash back to my younger years working for my dad’s remodeling business. Back then there was little awareness or thought given to the way we worked when disturbing lead paint. One summer I remember complaining of stomach aches, muscle pains and constantly feeling tired even after having the weekend off. My parents took me to the doctor but the doctor couldn’t find any reason for these symptoms. He gave me a terrible tasting medication to take daily and asked me to report back on how I was doing. The symptoms would seem to come and go all summer long, but then went away when I went back to college after the summer was over. This same scenario played over again the following summer. Fortunately for me, in the early days of owning my remodeling business, I learned a lot about lead and lead safe work practices through the NARI/HUD Lead Safe Remodeler training program that came out in the mid 1990’s. The current Certified Renovator training is only one day and really only teaches attendees how to contain the dust and debris. Different than the current class, the NARI/HUD class was two days long and actually thought us lead-safe work practices that eliminated or significantly reduced the creation of lead dust and debris. Attending that class was definitely worth the investment of time and money. Both I and my employees changed the way we thought about the work we did and the methods we used going forward.
Fortunately for me, in the early days of owning my remodeling business, I learned a lot about lead and lead safe work practices through the NARI/HUD Lead Safe Remodeler training program that came out in the mid 1990’s. The current Certified Renovator training is only one day and really only teaches attendees how to contain the dust and debris. Different than the current class, the NARI/HUD class was two days long and actually thought us lead-safe work practices that eliminated or significantly reduced the creation of lead dust and debris. Attending that class was definitely worth the investment of time and money. Both I and my employees changed the way we thought about the work we did and the methods we used going forward. Lead poisoning can occur when people are exposed to large or small amounts of lead over time. Lead builds up in the body and may cause temporary or permanent damage. A blood lead test can show whether your body has absorbed a dangerous amount of lead. A high blood lead level is an indication that lead is building up in the body faster than it can be eliminated.
Lead poisoning can occur when people are exposed to large or small amounts of lead over time. Lead builds up in the body and may cause temporary or permanent damage. A blood lead test can show whether your body has absorbed a dangerous amount of lead. A high blood lead level is an indication that lead is building up in the body faster than it can be eliminated. Later Signs and Symptoms:
Later Signs and Symptoms: On Friday
On Friday  If RRP instructors follow the EPA created instructor training manual when training renovators, they will be teaching students to do things that violate OSHA rules. (
If RRP instructors follow the EPA created instructor training manual when training renovators, they will be teaching students to do things that violate OSHA rules. ( Current OSHA and RRP related rules and training seems to concentrate on what not to do, without enough time and attention on the right way to do things. With OSHA for example, fall protection rules require a business to put fall protection equipment in place and train workers when and how to use. Great, but why not also complement it with training on methods for working safely and how to avoid putting yourself in a position to fall?
Current OSHA and RRP related rules and training seems to concentrate on what not to do, without enough time and attention on the right way to do things. With OSHA for example, fall protection rules require a business to put fall protection equipment in place and train workers when and how to use. Great, but why not also complement it with training on methods for working safely and how to avoid putting yourself in a position to fall?  For RRP, the required training teaches how to contain dust and debris so it won’t spread outside the contained work area. Might renovators who follow these instructions only be increasing the health risks to workers by containing and concentrating the dust and debris in the confined work area? Wouldn’t it make sense to also train workers on lead-safe work practices that actually limit or prevent the creation of dust to begin with?
For RRP, the required training teaches how to contain dust and debris so it won’t spread outside the contained work area. Might renovators who follow these instructions only be increasing the health risks to workers by containing and concentrating the dust and debris in the confined work area? Wouldn’t it make sense to also train workers on lead-safe work practices that actually limit or prevent the creation of dust to begin with?  The Lead and Environmental Hazard Association (LEHA)
The Lead and Environmental Hazard Association (LEHA)


 If an EPA enforcement employee and and OSHA Field inspector show up at one of your jobsites, at the same time, there is no way you will be able to satisfy both. I suggest this is another example of shortsighted leadership within both organizations. It also points out the lack of knowledge and awareness our political leaders in Congress have as it relates to understanding the construction industry and overseeing the creation of regulations that affect businesses of all sizes.
If an EPA enforcement employee and and OSHA Field inspector show up at one of your jobsites, at the same time, there is no way you will be able to satisfy both. I suggest this is another example of shortsighted leadership within both organizations. It also points out the lack of knowledge and awareness our political leaders in Congress have as it relates to understanding the construction industry and overseeing the creation of regulations that affect businesses of all sizes.





